What is a Certificate of Origin? Your Comprehensive Guide

The Certificate of Origin (CO) is one important document required for customs clearance in international trade. This document helps to verify the origin of your goods and can help you benefit from reduced tariffs during clearance.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explain all you need to know about the Certificate of Origin, its purpose, and the types available. Whether you’re a shipping expert or a newbie, this article will help you understand when and how to obtain this document to facilitate your clearance progress.
- What Is a Certificate of Origin?
- Importance of the Certificate of Origin?
- What Details are included in a Certificate of Origin?
- Types of COs
- Electronic vs. paper-based certificate of Origin
- How to obtain a Certificate of Origin?
- Who Issues Certificates of Origin?
- Do I always need a CO?
- Challenges with getting a Certificate of Origin
- FAQs
What Is a Certificate of Origin?
A Certificate of Origin (CO) is a shipping document that specifies the country where your goods were manufactured. It provides information about the origin of your product, its destination, and the exporting country.
Customs uses the certificate of origin to determine the appropriate tariffs that apply to your product. They can also use it to determine if you’re eligible for preferential import duties based on trade agreements with your exporting country. However, customs do not always require this document, depending on the importing country and the type of goods.
The CO is mostly issued by the exporter, and it is verified by the Chamber of Commerce in the exporting country. You should also know that the details in a CO must match those in the Commercial Invoice.
The importance of the Certificate of Origin?
Here are some reasons why this document is important in international trade:
- Determining tariffs: The CO helps customs authorities in the importing country apply the correct tariffs and duties to your goods.
- Enforcing trade agreements: Some countries have free trade agreements or other forms of preferential trade pacts with one another. The certificate of origin helps to confirm if your goods are eligible for reduced or free import duties.
- Quality control: The CO helps Customs determine if your goods meet the importing country’s regulations and safety standards. This is done to protect consumers and prevent unfair competition with domestic industries.
- Facilitating clearance: It facilitates easy clearance of your goods with customs.
- Statistics reference: It provides useful data when compiling international trade statistics between countries.
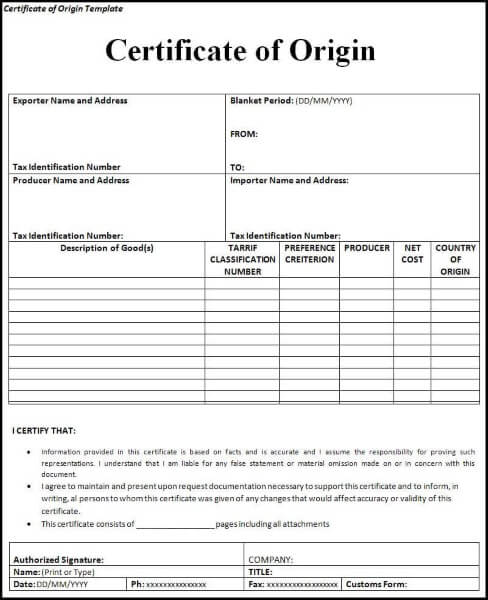
Details included in a Certificate of Origin
- Product description (size, quantity, and HS code.)
- Exporter or supplier’s name and company address.
- Country of Origin
- Consignees information (name and address)
- Port of origin and destination
- AWB/BOL number
- Exporter declaration
Types of Certificate of Origins
The two types of Certificates of Origin (COs) are:
Non Preferential COs
This is also known as an ordinary CO. It is used in regular international trade where no special trade agreements or reduced tariffs apply. Its purpose is simply to confirm the source of the goods.
This certificate certifies that your goods do not qualify for reduced tariffs or preferential treatment. Therefore, you may be charged VAT, anti-dumping duties, and excise duties.
Some countries impose sanctions on others and restrict the importation of their goods. Having a non-preferential CO is therefore important to allow customs to confirm that your goods do not originate from a restricted country.
Preferential COs
A Preferential Certificate of Origin is used when countries have special trade agreements in place. This may be a free trade agreement or a lower tariff deal. If you’re importing from one of such countries, you’ll be eligible for reduced import duties or tax exemptions.
The Preferential CO not only shows the country of origin but also states the specific trade agreement you’re eligible for. It tells customs that your products are part of a special trade deal and helps you claim the benefits.
A Preferential Certificate of Origin can save you money in international trade, but your goods must meet the import requirements of that country for you to enjoy the benefits.
The choice between these two types of COs depends on the trade relationship between the exporting and importing countries. When preferential trade agreements exist, you’ll benefit from reduced tariffs by using a Preferential Certificate of Origin. In the absence of such agreements, a Non-Preferential Certificate of Origin helps confirm the origin country of your product.
Electronic vs. paper-based certificate of Origin
There are two different approaches to handling the certificate of origin document. The traditional approach and the modern approach. Let’s explore the differences between them:
Paper-Based COs
This is the traditional and popularly used format. Paper-based COs involve physical documents that are printed, filled out manually, and authenticated by relevant authorities.
The exporter obtains a paper CO from an authorized party and submits it for verification at the Chamber of Commerce. After this, the exporter sends you the original copy and a photocopy. You then present the original to customs officials at the port, while you retain a copy for record’s sake. The exporter also keeps a copy of the document. To be accepted by customs, paper COs must remain valid for 12 months from their issuance date.
Processing paper COs can be time-consuming, as they need to go through different people for approval. Paper documents can also be easily misplaced, and are susceptible to errors like missing signatures or unreadable handwriting.
Electronic Certificates of Origin (e-CO)
Electronic COs (e-COs) are created and transmitted in digital formats, often as PDFs generated through specific platforms. An exporter fills out the necessary documents online and submits them electronically to the chamber of commerce for approval. After verification, the authorities stamp an electronic certificate and send it to the exporter within a day.
Many chambers of commerce worldwide are adopting e-COs as an innovative way to simplify export operations. It eliminates the need for physical visits and results in faster and more efficient certificate processing.
Electronic COs also reduce the risk of errors, as they come with standardized forms that ensure accuracy. You will find it much easier to store an electronic certificate than a paper-based form.
However, the use of Electronic COs is not as widespread as paper-based COs due to the special platforms required for uploading and verifying documents.
How to obtain a Certificate of Origin?
Obtaining a Certificate of Origin usually involves a series of steps. Here’s a simplified guide on how to get this document:
- First, determine if your goods require a CO.
- Find the relevant issuing authority. For most countries, this is the Chamber of Commerce. In China, it is provided by AQSIQ.
- Declare an affidavit stating you as the exporter.
- Provide the supplier’s invoice or commercial invoice to show where your goods originate from.
- Complete the CO application form. This includes your details and information about the country of origin.
- Submit the completed forms, invoice, and affidavit to the Chamber of Commerce. Ensure you state the documents you want stamped. You can do this in person or electronically, depending on the accepted approach.
- Pay the required stamp duties.
- Your application will be reviewed and approved usually within a few days. The CO is then stamped and provided to you.
- Keep the original and make extra copies. The certificate is usually valid for a year after issuance.
Some of these requirements may vary depending on the country, so it’s advisable to contact the local Chamber of Commerce to get precise guidance.
Who Issues Certificates of Origin?
Certificates of Origin (COs) are issued by designated authorities in the exporting country. In most countries, the local Chamber of Commerce is the primary authority responsible for issuing non-preferential COs.
Customs authorities or relevant government agencies are usually responsible for issuing preferential COs. In certain cases, certain third parties or industry-specific trade associations may also be authorized to issue COs. In rare instances, an exporter may be permitted to generate and certify a certificate of origin. These are called self-certified COs.

Do I always need a CO?
A Certificate of Origin (CO) may not be necessary every time you ship goods. Whether you need one depends on the type of goods and the trade agreement between the countries involved.
A certificate of origin is very valuable when you’re trading between countries with a free trade agreement or reduced tariffs. You should definitely request this document from your exporter in these cases. If you’re unsure about needing a CO for your shipment, then check with your customs authority.
Challenges with getting a Certificate of Origin
Here are some common hurdles exporters may face when applying for a certificate of origin:
- The documentation requirements for a CO can be complex and vary from country to country.
- The process of filling out forms and waiting for authentication may be time-consuming, especially for paper-based COs.
- Limited acceptance of electronic COs
- Errors in the application may lead to customs clearance delays.
- Most countries prefer the CO to be completed in English. This may cause mistakes for inexperienced exporters.
To overcome these challenges, you should stay informed about trade regulations or seek guidance from your local customs authorities. If you choose Winsky Freight as your freight forwarder, you don’t need to bother about these problems. Our team will help you swiftly process a certificate of origin and manage the customs clearance process.
FAQs
Which Countries need a Certificate of Origin?
All countries request a certificate of origin during import clearance. However, this certificate is not always required for every import. Ensure you check with customs authorities or ask your freight forwarder to determine when a CO is necessary.
Who can apply for a certificate of origin?
Only the exporter is required to apply for the Certificate of Origin. The exporter might be the seller or freight forwarder handling shipping for you. They must fill out the application form with information about the product’s origin and destination country.
Is a certificate of Origin expensive?
The cost of getting a CO depends on the country and issuing authority. However, it is usually a small fee charged for authenticating your certificate.
Can I use a single CO for goods from different Countries of Origin?
This depends on the regulations of the importing country. In certain countries, you may need to provide separate COs for each good. Meanwhile, in other countries, they may only request the CO from the last country you consolidated your goods.
Are there penalties for not meeting certificate of origin requirements?
Penalties for non-compliance with CO requirements mostly include customs delays, fines, or rejection of your goods. Request for help from a shipping expert to avoid such consequences.
Conclusion
Certificates of Origin (COs) play an important role in international trade. They help customs determine the appropriate rules and tariffs that apply to your goods, including your eligibility for preferential trade agreements. Knowing when and how to get one, as well as the different types available, makes your clearance process much easier.
It’s advisable to seek guidance from local customs authorities or trade experts when dealing with international shipments to ensure compliance and smooth transactions. If you’re ever uncertain about CO requirements, don’t hesitate to contact Winsky. Our team will provide expert guidance for all your shipping needs. We’re always happy to assist you!




Leave A Comment